
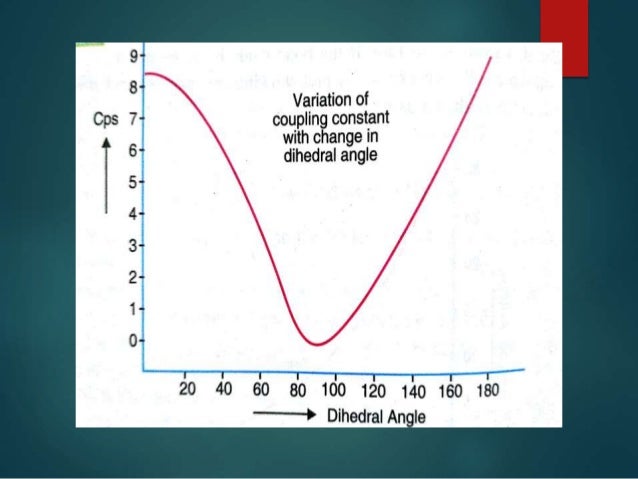
… Coupling between H atoms that are more than 3 bonds is also possible and is known as long range coupling. The coupling constant, J (usually in frequency units, Hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons. If it is a trans the J-Coupling constant of the unsaturated protons in the spectrum shows nearly 13-16 Hz, and it is nearly 10-12 in case of Cis isomers. Its very simple to determine the difference between Cis and Trans isomers by the help of Coupling constants in the 1H NMR spectra. What is the coupling constant J value for CIS? J or scalar coupling between magnetic nuclei (otherwise termed nuclear spins) is coupling via the intervening network of chemical bonds and depends on interaction between the nuclear spins and bonding electron spins. What does the J stand for in J-coupling?ĭefinition. Matching it up with other nearly-identical coupling constants elsewhere in the spectrum usually tells you which protons are near which others. The coupling constant J is pretty much the peak-to-peak distance, usually reported in Hz. The peaks within a triplet or quadruplet all have the same spacing, so you’ll only need to calculate this value once. If the second peak results in a value of 502.68, for example, the value for J would be 2.02 Hz. One-bond 13C- 1H correlations are easy to spot due to their large value and when joined with a straight line the corresponding cross-peaks form a forward slash "/".Arriving at J In a Duplet To calculate J for a duplet, simply subtract the lower value from the higher. The latter is determined based on the tilt of the cross-peaks, reminiscent to a COSY45 experiment for J HH couplings. The HSQC-HECADE experiment is unique in this regard as it allows to measure not only very small couplings, but also their sign. NMR experiments sensitive to the sign of the J coupling are rather rare. Thus, if we know that the sign of nJ CH is negative, then the number of bonds between C and H cannot be three and using the absolute value of the coupling constant we could make an educated guess on whether it corresponds to 2J CH or 4J CH. This has important implications for structure determinations of, for example, natural products, where no a priori assumptions can be made about atom connection pattern. It is well known that 13C- 1H couplings over one and three bonds ( 1J CH and 3J CH)are positive while those over two or four bonds ( 2J CH or 4J CH) are either positive or negative.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
